Respiratory system
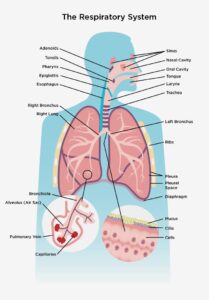
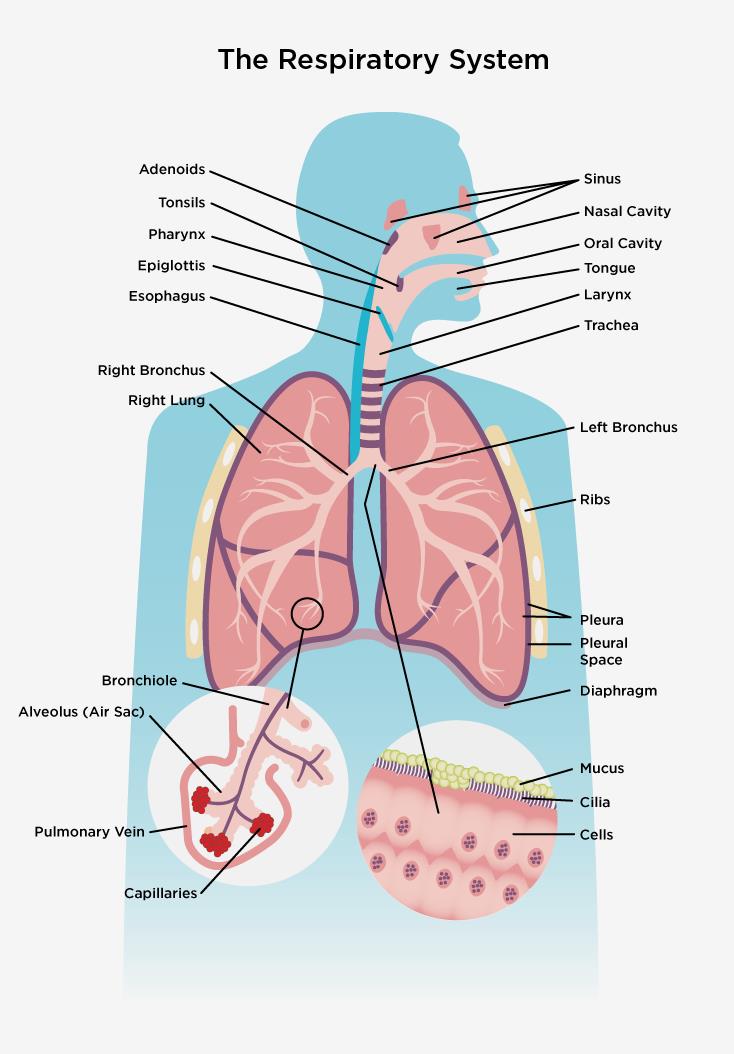
The major function of the respiratory system is to exchange oxygen and carbon-dioxide between the body and the environment. The gas exchange process itself take place in the respiratory divisions within the lungs. The rest of the respiratory system track the nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea, bronchi and bronchioles, essentially serve as passageways for air to flow in and out for air to flow in and out of the lungs and constitutes the conducting division.
https://www.highrevenuenetwork.com/tr0jpgwbui?key=5052565872a117d93b7167c78c7b6f68Nasal cavity:
The nasal cavity is lined within a ciliated mucus membrane. The sticky mucus traps inhaled particles, while the cilia drive debris-laden mucus toward the throat to be swallowed, inhaled bacteria are destroyed by lysozymes in the mucus, additionally protection against potential pathogens is provided by lymphocytes and anti-bacteria.
There are three folds of tissue arising from the wall of the nasal, conchae, or turbinate. These structures serve to increase the contact surface with inhaled air, enabling the nose to RAPIDLY warm, moisten and cleans it. The roof of the nasal cavity has a factory nerve cell in its living and is responsible for the sense of smell, from the nose, inhaled air turns 90 degrees downward as it reaches the pharynx.
This turn is another trap for large dust particles which because of their inertia crash into the posterior wall of the throat, and stick to the mucus.
The pharynx houses several tonsils. These immunocompetent tissues of the immune system are well positioned to respond to inhaled pathogens. In addition, to inhaled air, which is on its way to the lungs, the pharynx also passes foods and drinks from the mouth to the esophagus.
Because aspiration of food or drink into the lungs may potentially be life threatening. There is mechanism in placed to prevent this from happening. The larynx is most critical this regard. The opening of the larynx is guarded by a tissue flop called the epiglottis.
Integumentary system
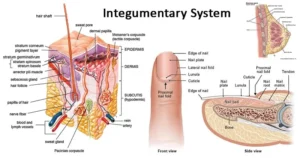
This body system is divided into three major parts
- The skin
- The hairs
- The nails
The skin:
This system is known as membrane because it covers the body or an organ, it contains several tissues. The skin is composed by three main layers.
- EPIDERMIS
- DERMIS
- HYPODERMIS
The hypodermis is the outer most layer of the skin, this layer is further divided into 5-6 thinner layers which do not have blood vessels, only two of these layers will be described.
- STRATIUM CORNEUM
This is the upper most layer of the skin which constantly sheds or where the dead skin cells are sloughed off. Essentially the top layer of the skin is composed of dead cells.
- STRATUM GERMINATIVUM
This is the lowest layer of the skin and it is contact with the dermis below. It is the layer in which cell division called mitosis take place and where new epidermis tissue is formed and begins to migrate to the surface of the skin.
Replacing the dead skin cells found in the stratum carenum.
- DERMIS
Dermis also known as the corium or the true skin, this layer contains major structure and functions for the skin within a framework of elastic connective tissue. This is where the skin comes to life, contained within the dermis are blood vessels, nerves, involuntary muscles, sweat glands, oil glands, hair follicles and the papilla.
THE DERMIS(CORNIUM)
Blood vessels via the capillary’s nutrients are provided to the skin and waste products are taken away. These blood vessels also play a major part in maintaining and sustaining the body’s temperature.
The vessels dilate (to make larger) release heat or they constrict (to make smaller) in order to the body heat.
INVOLUNTRY VESSELS IN THE DERMIS
They contract functions such as lifting hair or open pores by dilating or opening pores in the skin. The body is able to cool of and allow sweat to exit.
Hairs
The hair’s main function is to protect skin. Hair is composed of a strong structural protein called keratin. The hairs grow within a hollow tube called the follicle. more info athttps://yubloger.com/
NAILS
The nail’s main function is to save the fingers and toes as protective plates, and enhance the sensation or toe tip.
No Responses